Is the Biocomposites Boom Changing Industrial Design Forever?
The materials we use are quickly changing as the world focuses more on sustainability. Biocomposites stand out as a highly promising innovation. These materials mix natural fibers with polymers that are either biodegradable or bio-based. They are no longer just for scientists. Biocomposites are becoming central to national plans for clean manufacturing, growing rural economies, and building climate resilience.
Private companies are already using this for packaging, cars, and construction. Now, governments worldwide are stepping up with major research programs and large-scale projects. Let’s look at how the United States and India are driving this innovation through their official agencies and research labs.
🇺🇸 United States: From Research Lab to Real-World Industry
NSF’s Center for Bioplastics and Biocomposites (CB2)
The National Science Foundation (NSF) established CB2, a powerful research center at Iowa State University. This center is a partnership between universities and industry. It focuses on turning waste from farms and forests into valuable biobased products. These products include plastics, adhesives, and, importantly, biocomposites.
- Growing Focus: CB2 is now working hard on recycling and processing this after its use. This guarantees a circular and sustainable life cycle.
- Industry Ties: Big companies like John Deere and Medtronic are partners. They help bring research ideas into commercial use.
- Data Sharing: CB2 creates public databases on the properties of biocomposites. This helps manufacturers and researchers.
Why This Matters:
CB2 is fueling more than just invention, it’s also helping the economy. By using farm waste, the center creates new income for rural areas. It also reduces our need for oil-based materials.
DOE’s Biocomposites from Waste Biomass
The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE), through its Bioenergy Technologies Office (BETO), funds key research at Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL). This work focuses on making biocomposites from materials typically seen as waste.
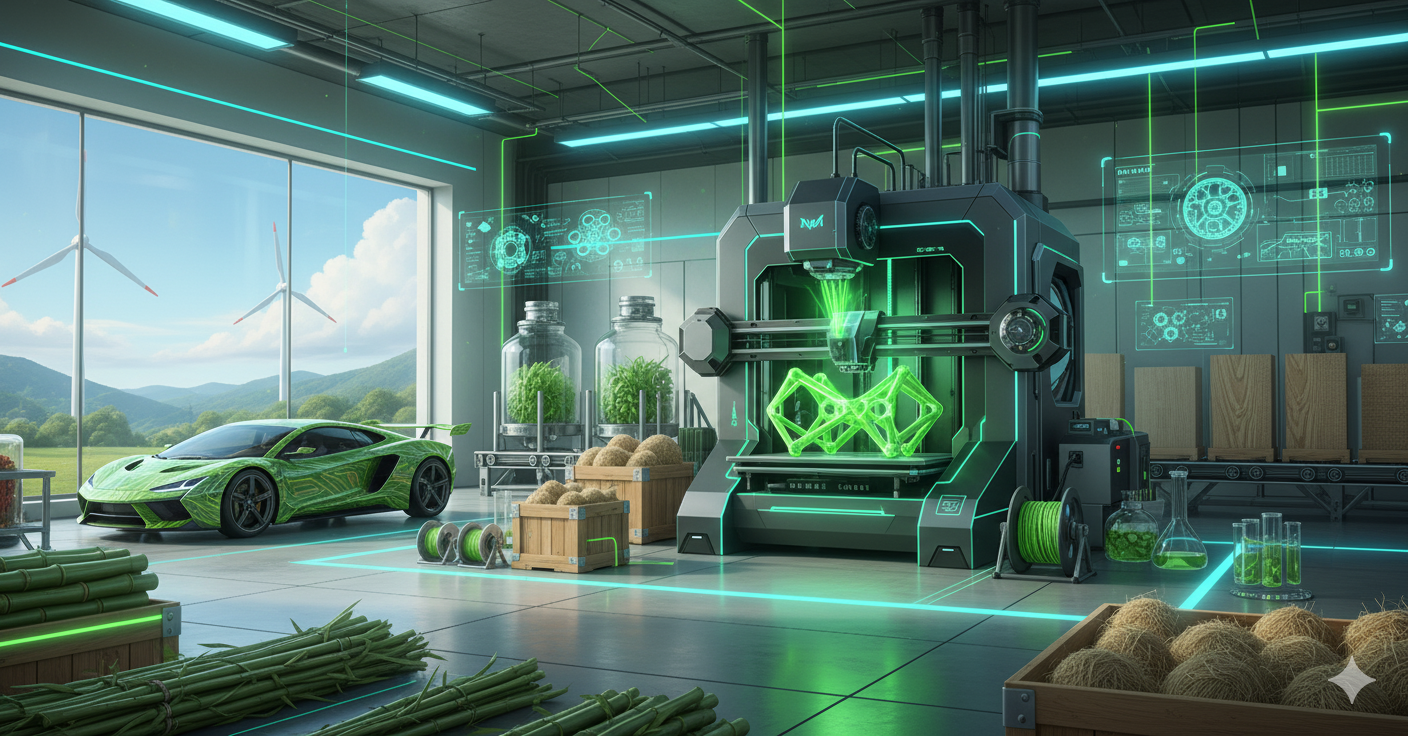
- Key Results: Researchers successfully made PLA-based. They are reinforced with low-grade fibers like switchgrass.
- High Performance: These new materials achieved 80% of the strength of carbon-fiber composites. However, they cost only about 25% as much.
- Advanced Use: Large-scale 3D printing tests using these new materials were successful.
Why This Matters:
This project proves that waste can become a high-performance material. This makes biocomposites both sustainable and affordable. It is a true win-win for both business and the planet.
USDA’s Forest Products Laboratory (FPL)
The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) is contributing through its Forest Products Laboratory (FPL). Their focus is on developing composites using wood and other natural fibers.
- Key Focus: FPL uses forestry and agricultural leftovers to create strong materials. These can be used in furniture, buildings, and infrastructure.
- New Fibers: They are exploring unconventional biofibers, even chicken feathers, for material reinforcement.
🇮🇳 India: Building the Eco-Materials Foundation
DRDO’s Research on Eco-Friendly Biocomposites
India’s Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has conducted major research. They partnered with institutions like ICAR and NERIST. Their focus is on fiber-reinforced bioplastics that can replace traditional glass fiber composites.
- Local Resources: The research highlighted jute and bamboo composites. Both fibers are abundant and renewable in India.
- Tackling Issues: They worked on solutions for fiber surface treatment and creating bionanocomposites.
- Purpose: The focus was on materials that are fully eco-compatible and easily break down. These are designed for both defense and public use.
Why This Matters:
This research established the base for India’s biocomposite industry. By using local natural fibers, India is moving toward self-reliance in sustainable materials science.
Global Vision: The Power of Biocomposites
Across both the US and India, similar goals drive the research efforts:
- Waste to Value: Governments are actively turning low-grade biomass, from corn husks to wood shavings, into useful inputs. This lowers costs and reduces waste.
- True Circularity: Projects like CB2 focus on clear end-of-life plans and recycling. This ensures materials remain green after they finish their job.
- Modern Methods: Using 3D printing is a huge step forward. It allows for quick, scalable production with green materials.
- Versatility: Biocomposites are being tested in many key areas. These include construction, vehicles, and defense. This proves they perform well across various sectors.
Final Thoughts: A Material Revolution Underway
Biocomposites offer more than a green substitute, they are a crucial national asset. Governments recognize their strong potential to spark innovation, lower environmental harm, and create new economic growth.
From the DOE using corn stover for large 3D prints to DRDO making defense materials from bamboo, the message is clear. Biocomposites are here to stay, and they are rapidly changing materials science. We are heading toward a future where our vehicles and buildings use materials that are high-performing and also planet-friendly. That is a truly great future worth building.